The File Associations module is used to create a mapping between a particular file extension and an associated executable, allowing you to control which default application should be started when using a certain file type. Optional command line options to use when running the executable can be specified as well. Admins can control which users are assigned which File Association rules by using Filters.
Filter
Select the name of the filter you want assigned to this configuration element. Click the Show Filter Details button on the right to review any filter settings without leaving Configuration Management.
Description
Enter a description for this rule.
Extension
Enter the file extension for which you are creating a mapping.
Executable
Enter the executable you want to associate with the extension.
Note: Some system applications like Notepad do not require a full path, just notepad.exe, while third party applications will require the full path: C:\Program Files\yourapp.exe.
Command Line Options
(Optional) Enter any command line options that the executable should use when running.
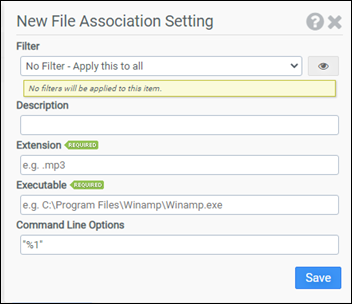
Example
This example will associate .mp3 files with the Winamp application.
- Filter: No Filter - Apply this to all
- Extension: .mp3
- Executable: C:\Program Files\Winamp\winamp.exe
For Modern Apps or apps installed from the Windows Store, you will need to provide the Application User Model ID (AUMID) rather than the full path of the desktop application executable. For example, the AUMID for Skype is Microsoft.SkypeApp_kzf8qxf38zg5c!App. The AUMID can be found several ways including using the Registry or PowerShell. When using the Registry, search for the AppUserModelID. When using Windows PowerShell, run the following script to list the AUMIDs installed on a desktop:
$installedapps = get-AppxPackage
foreach ($app in $installedapps)
{
foreach ($id in (Get-AppxPackageManifest $app).package.applications.application.id)
{
$line = $app.Name + " = " + $app.packagefamilyname + "!" + $id
echo $line
}
}